Understanding the Challenges of Financing Modular Construction: A Case Study for Prospective Multifamily Units
A recent report by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) explores the financial challenges developers face when using modular construction for multifamily projects. Modular construction, while faster and often cheaper than traditional methods, requires significant upfront capital. Developers must secure large deposits months before production, leading to higher equity requirements. Additionally, some lenders view modular projects as riskier, sometimes resulting in higher interest rates and lower loan-to-cost ratios.
However, modular construction shortens building timelines by up to six months, improving income generation and offering consistent quality control.
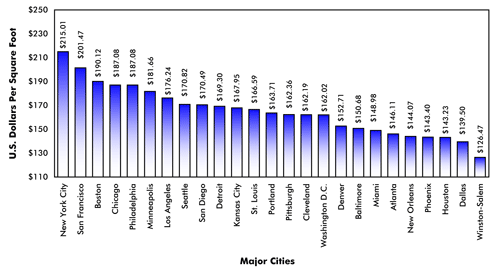
Credit: (NREL 2022)
Key Findings:
- Upfront Capital Needs
Modular construction typically requires large deposits months before production begins. This increases developers’ equity requirements. - Financing Risks
Lenders often consider modular construction risky because a significant portion of work happens offsite. Therefore, they may offer lower loan-to-cost ratios and higher interest rates. - Cost and Time Savings
Despite financing challenges, modular construction can reduce construction timelines by up to 40%. It also provides consistent quality control and lowers overall costs through standardization and reduced project overruns.
Case Study Comparison:
The report compared two 200-unit multifamily projects: one built traditionally and one using modular techniques. Modular construction reduced the timeline by six months, saving on costs related to labor and materials. However, modular developers needed 30% more equity upfront due to line reservation fees and material deposits, which were required three to six months before construction.

Photo credit: ProSet Inc.
Solutions and Recommendations:
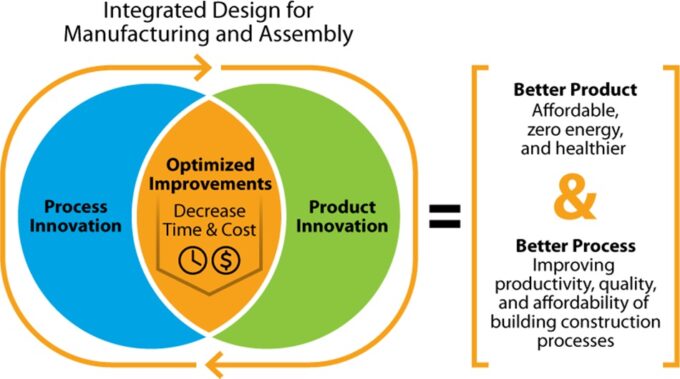
The study highlights alternative financing methods, including partnerships with lenders familiar with modular construction. Additionally, the report calls for greater standardization and state-supported housing funds to address financing gaps. Future research is recommended to explore incentives that could help scale modular construction and lower financial risks for developers.
Modular construction offers numerous benefits, but financing hurdles remain a barrier to its widespread adoption. Understanding and addressing these challenges could pave the way for faster, more affordable, and sustainable housing projects.
For more details, refer to the full NREL report.