What Is Acoustic Separation in Buildings?
Acoustic separation refers to the design and construction measures used to prevent sound transmission between spaces in a building. This ensures privacy and reduces noise disturbances, enhancing occupant comfort. Effective acoustic separation is essential in residential, commercial, and mixed-use developments, especially where different noise-sensitive activities coexist.
What Is STC?
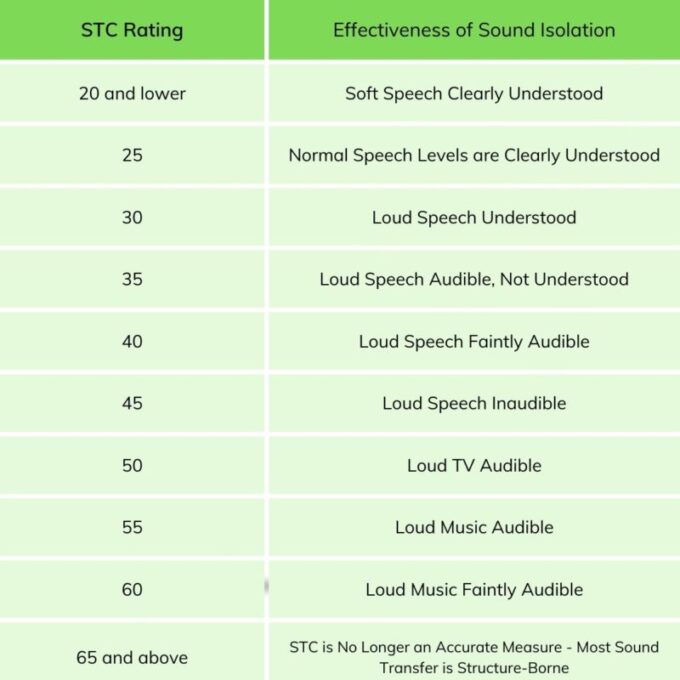
Sound Transmission Class (STC) is a standardized rating that measures an assembly’s ability to reduce airborne sound. Higher STC ratings indicate better sound insulation. The STC value helps compare the effectiveness of walls, floors, ceilings, and other barriers in blocking noise.
- How Is STC Determined?
STC is calculated in a controlled lab environment using sound waves of varying frequencies. Technicians measure how much sound passes through an assembly. The results create a curve that determines the STC rating. Real-world conditions, however, can lead to slightly different performance. - Examples of STC Ratings:
- STC 25: Normal speech can be heard and understood.
- STC 50: Loud speech is inaudible but some impact noises may still be perceptible.
- STC 60+: Almost complete sound isolation, ideal for high-performance spaces.
Code Requirements
Building codes set minimum STC ratings for different building types to ensure acceptable acoustic performance. For example:
- Residential Buildings: The International Building Code (IBC) mandates a minimum STC of 50 for walls, floors, and ceilings between dwelling units.
- Commercial Spaces: Specific requirements depend on building use but often align with privacy needs, such as in hospitals or offices.
Best Practices for Acoustic Separation in Buildings
- Select the Right Materials:
Use dense materials like concrete, mass-loaded vinyl, or sound-rated drywall to enhance sound insulation. - Decouple Structures:
Create independent assemblies (e.g., staggered studs or resilient channels) to reduce sound transfer through direct connections. - Seal Gaps and Penetrations:
Seal all gaps, including around outlets, ductwork, and edges, with acoustical caulking or gaskets. - Incorporate Sound-Absorbing Layers:
Add fiberglass insulation, acoustic panels, or sound blankets within wall or floor assemblies for added isolation. - Minimize Impact Noise:
Use underlayments, carpets, or floating floors to reduce vibrations and noise caused by footfall or equipment.
Importance of Experienced Designers
Soundproofing requires precise knowledge of materials, construction techniques, and building codes. Experienced designers and engineers optimize acoustic performance by balancing cost, aesthetics, and functionality. They also ensure compliance with regulations while meeting the specific needs of each project.
Benefits of Proper Acoustic Design
- Enhanced Privacy: Improves satisfaction for residents, office workers, and hospitality guests.
- Improved Health: Reduces stress and enhances focus by minimizing noise disturbances.
- Increased Property Value: High acoustic performance adds value and appeal to buildings.
Partnering with Experts
At EVstudio, our team has extensive experience in designing acoustically optimized buildings. We tailor solutions to your project’s specific needs, ensuring a balance of performance and cost-efficiency. Whether you’re planning a residential, commercial, or mixed-use project, our expertise can help you achieve outstanding results.
For more information on acoustic standards and best practices, consult these resources:
Elevate your project’s acoustic performance with a professional team that understands the science and art of sound. Contact EVstudio today!