Electrical Engineering Glossary for Building Construction
EVstudio’s world-class team of electrical engineers delivers innovative, efficient, and reliable electrical system designs tailored to every project. Our expertise ensures optimized performance, energy efficiency, and safety. From power distribution to lighting systems, we provide exceptional value to our clients. Below is a glossary of 50 essential terms and acronyms used in electrical engineering for building construction.
- Ampere (Amp)
Unit of electric current measuring the flow of electrical charge. - Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI)
Device preventing fires by detecting and interrupting dangerous electrical arcs. - Backup Generator
Equipment providing power during outages or emergencies. - Ballast
Device regulating current to fluorescent or HID lamps for stable operation. - Busbar
Conductive strip distributing electrical power within switchboards or panels. - Circuit Breaker
Safety device interrupting electrical flow during overloads or faults. - Class 1, 2, and 3 Circuits
Categories of circuits based on voltage, current, and safety requirements. - Conductor
Material, typically copper or aluminum, carrying electrical current. - Current Transformer (CT)
Instrument measuring current and providing input for metering or protection systems. - Demand Load
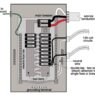
The maximum electrical power required at a specific time. - Distribution Panel
Panel dividing electrical power into subsidiary circuits. - Emergency Lighting
Lighting providing illumination during power failures for safety. - Energy Management System (EMS)
System monitoring and optimizing energy consumption in buildings. - Feeder
Electrical circuit transmitting power from a source to a distribution point. - Fuse
Safety device breaking a circuit when excessive current flows. - Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI)
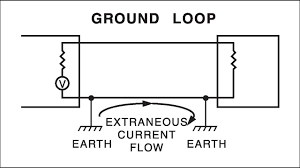
Device protecting people from electrical shock by detecting ground faults. - Grounding
Connection of electrical systems to the earth for safety. - Harmonics
Electrical distortions in power systems caused by nonlinear loads. - High-Intensity Discharge (HID) Lighting
Efficient lighting technology for large spaces like warehouses. - Illuminance
Measure of light intensity falling on a surface, expressed in lux. - Impedance
Resistance and reactance opposing current flow in AC circuits. - Inrush Current
High initial current drawn when electrical equipment starts. - Interrupting Rating
Maximum fault current a circuit breaker or fuse can safely interrupt. - Junction Box
Enclosure housing electrical connections and protecting wiring. - Kilovolt-Ampere (kVA)
Unit measuring apparent electrical power in AC systems. - Light-Emitting Diode (LED)
Energy-efficient, long-lasting lighting technology for modern buildings. - Lighting Control System
System automating and optimizing building lighting for energy efficiency. - Load Calculation
Process determining the electrical power needed for a building or system. - Low Voltage
Electrical systems operating at 50 volts or less. - Lumen
Unit measuring the total visible light output of a source. - Megawatt (MW)
Unit of power equal to one million watts. - Metering
Measurement of electrical energy usage for monitoring and billing. - National Electrical Code (NEC)
Standard governing safe installation of electrical systems in the U.S. Also known as NFPA 70 - Ohm
Unit of electrical resistance opposing current flow. - Overcurrent Protection Device (OCPD)
Equipment, like fuses or breakers, preventing overload damage. - Panelboard
Component distributing electrical power to various circuits. - Photovoltaic (PV) System
Solar energy system converting sunlight into electrical power. - Power Factor
Ratio of real power to apparent power, indicating electrical efficiency. - Raceway
Enclosure protecting and routing electrical wires or cables. - Receptacle
Outlet providing power to plug-in devices or appliances. - Relay
Switch controlling circuits using low-power signals. - Residual Current Device (RCD)
Device detecting leakage currents and preventing electrical shock. - Short Circuit
Fault condition causing excessive current flow between conductors. - Single-Line Diagram
Simplified drawing illustrating an electrical power distribution system. - Surge Protection Device (SPD)
Equipment safeguarding electrical systems from voltage spikes. - Transformer
Device converting electrical voltage levels for transmission or distribution. - Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)
System providing temporary backup power during outages. - Volt (V)
Unit measuring electrical potential or pressure in a circuit. - Watt (W)
Unit measuring electrical power or energy consumption. - Wire Gauge
Standardized measurement determining the diameter of electrical wires.
At EVstudio, our experienced electrical engineers design reliable, efficient, and cutting-edge electrical systems for buildings of all types. We prioritize safety, energy optimization, and long-term performance to deliver unmatched client value. Reach out to EVstudio for your next electrical design project.