Intumescent Paint: Fire Protection with Modern Applications
Intumescent paint plays a crucial role in fire protection for building structures, combining innovation with safety standards. This article covers what intumescent paint is, how it works, where it’s applied, and why it’s become increasingly relevant in building design. Additionally, we’ll review its advantages and challenges, manufacturers, and future adoption trends within building codes. Using Intumescent Paint for Fire Protection is a critical tool in the design toolbox for residential commercial applications.
What is Intumescent Paint?
Intumescent paint is a fire-protective coating designed to expand when exposed to high temperatures, creating a char-like layer that insulates the surface beneath. In building construction, intumescent paint primarily protects structural steel and other load-bearing materials from reaching critical temperatures during a fire, delaying potential structural failure and providing critical time for evacuation and fire response.
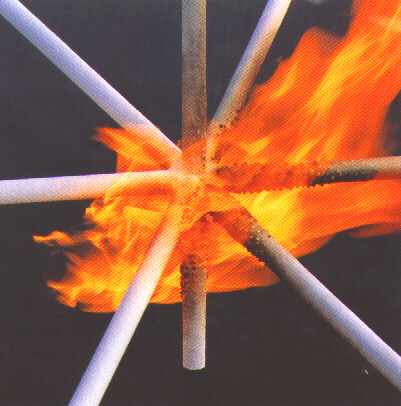
Before and After flame application and char development of intumescent paint
How Does Intumescent Paint Work?
Intumescent paint works by undergoing a chemical reaction at high temperatures. When temperatures reach around 400°F (204°C), the paint begins to expand, or “intumesce,” increasing its volume and forming an insulating foam-like barrier. This expansion, often up to 50 times the original thickness, reduces heat transfer to the structural elements. The charred layer insulates and protects the underlying materials, preserving structural integrity during intense fire conditions.
Applications of Intumescent Paint in Construction
In construction, intumescent paint is used across a variety of applications where fireproofing is critical, including:
- Steel Structures: Steel beams and columns are common in commercial buildings. Intumescent paint prevents these elements from reaching temperatures where they lose strength.
- Wood Structures: Used less commonly on wood, but effective in slowing down burning rates, particularly in residential buildings.
- Ductwork: Coating ducts in intumescent paint reduces the risk of fire spread through HVAC systems.
- Electrical Conduits and Pipes: Helps prevent fire from spreading through utility conduits, adding an extra layer of protection to critical systems.
Pros and Cons of Intumescent Paint
Pros
- Fire Resistance: Provides effective fire protection by delaying the temperature rise of structural components.
- Aesthetic Flexibility: Unlike concrete or bulky fireproof cladding, intumescent paint maintains the original look of the structure.
- Lightweight Solution: Adds minimal weight to structural elements, making it suitable for various building types.
- Non-Toxic Fumes: Many intumescent coatings are designed to emit low-toxicity fumes when exposed to high heat, improving occupant safety.
Cons
- Higher Cost: Intumescent paint is generally more expensive than traditional fireproofing methods.
- Regular Maintenance Required: Periodic inspections and touch-ups are essential to ensure continued fire resistance.
- Limited Durability in High-Moisture Areas: Moisture can impact the paint’s longevity, necessitating protective topcoats in humid environments.
- Application Skill Required: Proper application demands trained professionals to achieve uniform thickness and coverage.
Future of Intumescent Paint in Building Codes
With rising focus on building safety and sustainable design, intumescent paint is gaining attention from building code developers. Currently, many local and national codes recognize intumescent coatings as an acceptable form of fireproofing, especially for structural steel. However, uniform guidelines for application and maintenance standards are still developing. As environmental concerns grow, newer intumescent coatings focus on eco-friendly formulations, which could lead to more widespread adoption in green building codes.
Manufacturers of Intumescent Paint
Several manufacturers specialize in high-quality intumescent paints, each offering products tailored to various applications and environmental conditions:
- Sherwin-Williams: Known for its Firetex line, which offers coatings suitable for steel structures.
- AkzoNobel: Offers a line of intumescent paints under the Interchar brand, commonly used for commercial steel structures.
- PPG Industries: PPG’s Steelguard is popular in industrial and commercial applications.
- Carboline: Provides intumescent coatings like Pyroclad, widely used in structural fire protection.
To find intumescent paint for a project, consult local distributors or visit these manufacturers’ websites for certified sellers. Many large paint retailers, such as Sherwin-Williams and PPG stores, also provide intumescent options upon request.
Integrating Intumescent Paint into Your Project
To incorporate intumescent paint into a construction project, first consult with an Architect, Structural Engineer or Fire Protection Specialist to determine specific requirements. Certified professionals will assess the structure’s fire resistance needs and recommend the appropriate coating thickness. Additionally, local building code officials can advise on compliance to ensure the project meets regional safety standards.
Intumescent paint can be applied using spray equipment or roller brushes, but always ensure proper training and certification of applicators to achieve consistent coverage. Coordinating with manufacturers or certified distributors can further streamline the sourcing and application process.
Conclusion
Intumescent paint is a powerful tool for fire protection, combining safety with design flexibility. Its role in preserving structural integrity and delaying heat transfer makes it ideal for modern construction, particularly in high-rise and commercial settings. While it requires professional application and regular upkeep, intumescent paint’s benefits for aesthetics, weight, and safety make it a valuable choice. With increased environmental focus and code development, intumescent paint will likely see greater adoption in fire-resistant building design.
References
- Sherwin-Williams Firetex line: Sherwin-Williams
- AkzoNobel Interchar intumescent coatings: AkzoNobel
- PPG Steelguard line: PPG Industries
- Carboline Pyroclad: Carboline