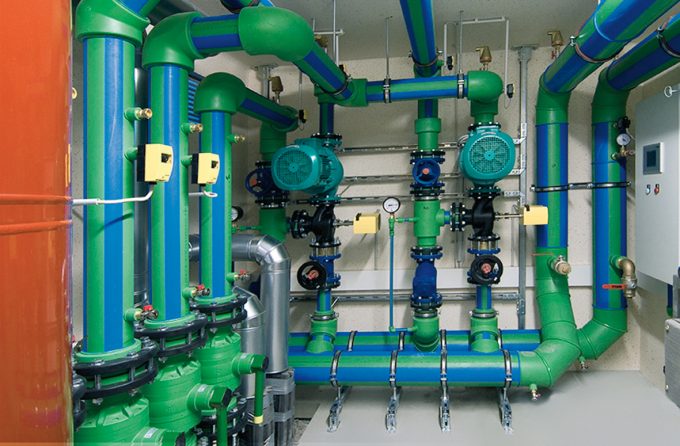
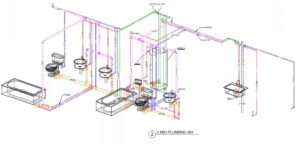
Plumbing Design Glossary: Top 50 Terms and Acronyms
At EVstudio, our world-class team of engineers specializes in innovative and efficient plumbing designs for all building types. From water conservation to complex system integrations, we provide tailored solutions that meet client needs and comply with codes. This glossary highlights key terms and acronyms specific to plumbing design, demonstrating the expertise we bring to every project.
- ADA Fixtures
Plumbing fixtures compliant with the Americans with Disabilities Act, designed for accessibility and usability by all individuals. - Air Admittance Valve (AAV)
A valve allowing air into the plumbing system to equalize pressure without venting through the roof. - Anti-Siphon Valve
A device preventing backflow into the water supply by blocking reverse water movement. - Backflow Preventer
A device stopping contaminated water from flowing back into the potable water supply. - Ball Valve
A shutoff valve with a rotating ball that controls water flow within pipes. - Branch Line
A secondary pipe distributing water or drainage from a main supply or waste line. - Building Drain
The lowest point of a drainage system where all building fixtures connect before discharging to a sewer or septic. - Building Sewer
The underground pipe carrying wastewater from the building drain to the public sewer or septic system. - Cast Iron Pipe
Durable piping material commonly used for drainage, waste, and vent systems in commercial buildings. - Cleanout
An access point in plumbing systems for clearing clogs or performing maintenance on drainage pipes. - Code Compliance
Adherence to local, state, and national plumbing codes ensuring safety and functionality of systems. - Cross-Connection
A physical link between potable water systems and potential contaminants, addressed by backflow prevention devices. - Curb Box
A protective housing for shutoff valves located at the street for water service lines. - Demand Load
The total anticipated water or drainage usage in a building under normal operating conditions. - Drain-Waste-Vent (DWV) System
A plumbing system removing wastewater and venting sewer gases safely from a building. - Expansion Tank
A device compensating for water expansion in heating systems to prevent pressure buildup. - Fixture Unit (FU)
A measure of water usage demand assigned to plumbing fixtures for system design purposes. - Flushometer Valve
A valve delivering high-pressure water to commercial toilets or urinals without using a tank. - GPM (Gallons Per Minute)
A unit measuring water flow rate, used to size plumbing fixtures and pipes. - Graywater
Gently used water from sinks, showers, or laundry reused for irrigation or non-potable applications. - Grease Interceptor
A device capturing grease and solids from wastewater to protect sewer systems. - Hot Water Return Line
A pipe returning unused hot water to the heater for energy-efficient recirculation. - Hydraulic Calculations
Mathematical analysis ensuring adequate pipe sizing and flow rates within a plumbing system. - Isolation Valve
A valve used to shut off water flow to a specific section of a plumbing system. - Main Line
The primary pipe distributing water or removing waste within a building’s plumbing system. - Manhole
An access point for inspecting or maintaining underground sewer or drainage systems. - PEX (Cross-Linked Polyethylene)
Flexible plastic piping material commonly used for water supply systems. - Plenum
A space used to distribute conditioned air, often requiring special piping materials for fire resistance. - Potable Water
Water safe for drinking and cooking, supplied through certified plumbing systems. - Pressure Reducing Valve (PRV)
A valve regulating water pressure to prevent damage to plumbing systems and fixtures. - Riser
A vertical pipe distributing water, gas, or drainage between floors in multi-story buildings. - Roof Drain
A plumbing fixture collecting and directing rainwater from roofs to drainage systems. - Sanitary Sewer
A system carrying wastewater from buildings to treatment facilities or septic systems. - Septic Tank
A buried tank treating wastewater from buildings not connected to a municipal sewer system. - Service Line
A pipe connecting the building’s water system to the municipal water main. - Siphon Breaker
A device preventing siphoning of wastewater into potable water systems. - Soil Pipe
A pipe carrying human waste from toilets to the building drain or sewer. - Storm Sewer
A separate system carrying rainwater and storm runoff away from buildings and streets. - Sump Pump
A pump removing accumulated water from a sump basin, typically found in basements. - Tankless Water Heater
An on-demand water heater providing hot water without a storage tank, improving energy efficiency. - Trap
A U-shaped pipe preventing sewer gases from entering a building through drains. - Trap Primer
A device ensuring water remains in traps to maintain their seal against sewer gases. - Vacuum Breaker
A valve preventing back-siphonage of contaminants into potable water systems. - Vent Stack
A vertical pipe venting sewer gases and maintaining proper air pressure in plumbing systems. - Water Hammer
A hydraulic shock in pipes caused by sudden changes in water flow or pressure. - Water Main
A large pipe delivering water from the municipal supply to individual buildings. - Water Meter
A device measuring water usage for billing and monitoring purposes. - Water Softener
A system removing hard minerals from water to prevent scale buildup in plumbing systems. - Wet Vent
A vent pipe also carrying drainage, designed to serve both functions in a plumbing system. - Zone Valve
A valve controlling water flow to specific zones in hydronic heating or cooling systems.
EVstudio’s expertise in plumbing design ensures efficient, sustainable, and code-compliant systems tailored to your building’s needs. Contact us to discuss how we can enhance your project!