The Science Behind Pre-Engineered Metal Buildings (PEMB) for Industrial Buildings
Pre-Engineered Metal Buildings (PEMB) offer a modern, efficient approach to constructing industrial facilities. Engineers design these buildings with a pre-determined framework, allowing quick assembly on-site. PEMB construction has gained popularity for its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and speed. This article will explore the science behind PEMB construction, its ideal project applications, advantages, disadvantages, and how it compares in cost to other construction methods.
What is PEMB Construction?
In PEMB construction, engineers design and fabricate metal components, such as beams, columns, and roof trusses, off-site. They use computer-aided design (CAD) to create precise specifications for each component. Once fabricated, these components are transported to the construction site for assembly. The building is essentially a kit, where workers bolt the pre-engineered parts together, ensuring a quick and efficient construction process.

Ideal Project Types
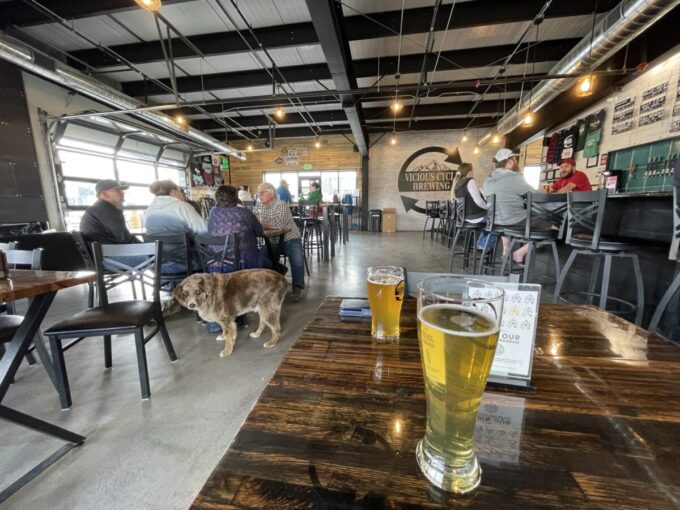
PEMB construction works best for industrial projects that require large, clear-span spaces. Warehouses, factories, distribution centers, and agricultural facilities often use PEMBs because they provide open interiors without the need for internal support columns. This flexibility allows for efficient use of space, making it ideal for storage, manufacturing, and other industrial operations that require large, unobstructed areas. And even breweries (as shown above)!
Differences from Other Construction Methods
PEMB construction differs significantly from traditional building methods. Unlike conventional construction, which often involves on-site fabrication and assembly of materials like wood or concrete, PEMB relies on pre-engineered components. In traditional steel construction, workers cut and weld steel beams on-site, which requires more time and labor. In contrast, PEMB components arrive at the site ready for assembly, reducing both construction time and labor costs.
Advantages of PEMB Construction
- Cost-Effectiveness: PEMB construction typically costs less than traditional methods. The pre-engineered components reduce material waste and lower labor costs. According to research, PEMB can reduce construction costs by up to 30% compared to traditional steel construction (source: National Institute of Building Sciences).
- Speed of Construction: Pre-engineering and off-site fabrication significantly speed up the construction process. You can assemble PEMBs in a fraction of the time it takes to build traditional structures.
- Design Flexibility: PEMBs offer design flexibility. Engineers can customize building dimensions, layouts, and aesthetics to meet specific project needs.
- Durability and Low Maintenance: PEMBs are durable and resistant to fire, pests, and severe weather. The metal components require minimal maintenance, reducing long-term operational costs.
Disadvantages of PEMB Construction
- Limited Customization: While PEMBs offer flexibility, they may not be suitable for projects that require highly customized designs or intricate architectural details. The modular nature of PEMBs can limit design options.
- Initial Design Costs: The initial design phase may involve higher costs due to the need for precise engineering and fabrication. However, these costs are often offset by the savings during construction.
- Transport and Logistics: Transporting large metal components to the site can be challenging, particularly for remote or difficult-to-access locations.
Cost Comparison
PEMB construction is generally more cost-effective than traditional methods. Research indicates that PEMBs can save up to 30% on total construction costs compared to conventional steel or concrete structures. These savings come from reduced labor, material efficiency, and quicker project completion. Additionally, PEMBs often result in lower long-term maintenance costs due to their durability and resistance to wear.
Conclusion
Pre-Engineered Metal Buildings provide a practical, cost-effective solution for industrial construction. Their ability to deliver large, open spaces quickly and efficiently makes them ideal for warehouses, factories, and other industrial uses. While PEMBs have some limitations in design flexibility, their advantages in cost, speed, and durability often outweigh these drawbacks. By understanding the science behind PEMB construction, project stakeholders can make informed decisions that align with their specific industrial building needs. Understanding the science and benefits of PEMB construction allows project managers to choose the best approach for their industrial building projects. If you are considering the construction type for your next project, reach out to our team of expert Architects and Engineers and we would be happy to help you evaluate the best options.
References
- National Institute of Building Sciences. (n.d.). Cost-Effective Solutions with Pre-Engineered Metal Buildings. Retrieved from National Institute of Building Sciences
- American Institute of Steel Construction. (2022). Comparative Analysis of PEMB and Traditional Steel Construction. Retrieved from AISC