Understanding Decarbonized Concrete: The Future of Sustainable Building Materials
Concrete is a foundational material in construction, yet its production contributes significantly to carbon emissions worldwide. Decarbonized concrete aims to address this by reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional concrete. By leveraging new materials and production processes, decarbonized concrete offers builders a sustainable alternative for various applications, from infrastructure to residential projects. Understanding Decarbonized concrete is key to understanding sustainable building technology.
What Is Decarbonized Concrete?
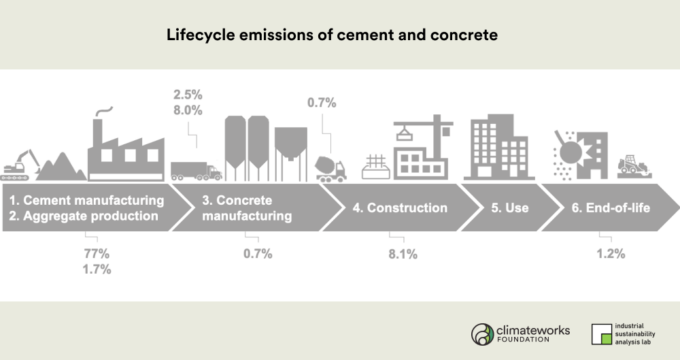
Decarbonized concrete is concrete produced with methods and materials that minimize carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions. Traditional concrete production is carbon-intensive, mainly due to the cement manufacturing process, which accounts for about 8% of global CO₂ emissions. Decarbonized concrete reduces or even eliminates this carbon output by substituting traditional cement with eco-friendly alternatives, using recycled materials, or optimizing production processes.
How Decarbonized Concrete Is Made
Manufacturers produce decarbonized concrete by altering the composition and production processes associated with conventional concrete. Below are some primary methods:
- Replacing Traditional Cement: One method replaces Portland cement with supplementary materials like fly ash, slag, or calcined clay, which emit less CO₂.
- Carbon Capture and Utilization (CCU): CCU technologies inject captured CO₂ directly into the concrete during mixing, permanently sequestering carbon in the concrete matrix.
- Alkaline-Activated Cementitious Material (AACM): This process uses alternative binders, such as ground granulated blast-furnace slag (GGBS) or fly ash, activated by alkaline solutions, to reduce emissions.
- Recycled Aggregates: Using recycled materials as aggregates decreases the demand for raw materials and reduces the embodied carbon of the concrete.
These innovations collectively reduce carbon emissions and increase the environmental sustainability of concrete used in construction.
Applications of Decarbonized Concrete
Decarbonized concrete can be used in almost any project where traditional concrete is suitable. Popular applications include:
- Structural Components: Beams, columns, and load-bearing walls in commercial and residential buildings.
- Infrastructure: Roadways, bridges, and other public infrastructure projects.
- Pavement and Sidewalks: Footpaths, patios, and non-structural paving.
While still in its early adoption stages, decarbonized concrete is gaining traction as more manufacturers and projects strive for sustainability.
Pros and Cons of Decarbonized Concrete
Decarbonized concrete offers multiple benefits, but there are also some limitations to consider:
Pros
- Lower Carbon Footprint: Reduces the environmental impact associated with cement production and lowers overall CO₂ emissions.
- Durability: Many types of decarbonized concrete are as durable, if not more so, than traditional concrete.
- Resource Efficiency: Recycled materials in decarbonized concrete reduce reliance on raw resources and minimize waste.
- Compatibility: Works with various applications in construction, making it suitable for both large and small-scale projects.
Cons
- Cost: Decarbonized concrete may cost more than traditional concrete due to specialized materials and production processes.
- Availability: Limited supply and manufacturing facilities make it less accessible in some regions.
- Performance Variability: Depending on the specific formulation, some decarbonized concrete may perform differently than traditional concrete, especially in strength or curing times.
How Decarbonized Concrete Compares to Standard Concrete
In terms of performance, decarbonized concrete generally holds up well against standard concrete. Its durability and strength can match or even surpass that of traditional concrete, depending on the formulation. Decarbonized concrete often has faster curing times, especially when using carbon-sequestration methods, which can enhance project timelines. However, the availability and cost factors can vary by region, making decarbonized concrete less accessible than traditional options.
Manufacturers of Decarbonized Concrete
Several manufacturers have pioneered decarbonized concrete production:
- CarbonCure Technologies: Known for its CCU technology, CarbonCure infuses captured CO₂ into concrete during mixing, sequestering carbon.
- Ecocem: This company specializes in low-carbon, GGBS-based cement, reducing emissions associated with cement production.
- Solidia Technologies: Offers a proprietary cement that reduces CO₂ emissions and captures additional carbon during curing.
- CarbiCrete: A carbon removal technology company that enables the production of cement-free, decarbonized concrete.
To find decarbonized concrete locally, reach out to these manufacturers or consult regional suppliers partnered with sustainable construction companies.
The Importance of Choosing Decarbonized Concrete for Sustainable Construction
Decarbonized concrete offers a path to more sustainable construction without sacrificing performance. Its ability to reduce emissions, sequester carbon, and provide durability makes it a valuable material for forward-thinking projects. Although it comes with certain limitations, the environmental benefits and growing market for decarbonized concrete signal a significant shift in how the construction industry approaches sustainability.