The Impact of Federal Interest Rates on Development Costs
Rising federal interest rates are increasing the cost of financing, making development more expensive for building owners and developers. Higher borrowing costs affect project feasibility, slow new construction, and reduce investment returns. Understanding these impacts helps industry professionals adapt and manage financial risks.
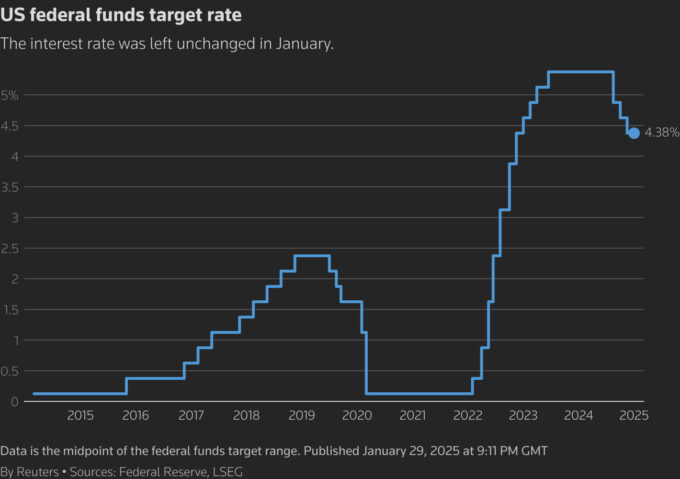
Why Interest Rates Are Rising
The Federal Reserve raises interest rates to control inflation and stabilize the economy. When inflation spikes, the Fed increases rates to slow spending and borrowing. Since 2022, the Fed has implemented aggressive rate hikes, pushing borrowing costs to their highest levels in over two decades. Fortunately, towards the end of 2024, the fed began slowly lowering the rates, easing the lending crisis it created in development. However the first fed meeting of 2025 resulted in no change.
Example: The Federal Funds Rate jumped from near 0% in early 2022 to over 5% by 2023, significantly increasing lending costs (Federal Reserve, 2023).
How Higher Interest Rates Impact Development Costs
1. Increased Construction Loan Costs
Developers rely on loans to finance projects. Higher interest rates mean higher monthly payments, reducing cash flow and profitability.
Example: A $10 million construction loan at 4% interest costs $400,000 annually. At 8%, that cost doubles to $800,000.
2. Reduced Project Feasibility
Many projects become financially unviable as financing costs rise. Developers either delay construction, reduce project scope, or cancel plans.
Example: A mixed-use development in Texas was postponed after interest rate hikes pushed financing costs 30% over budget (GlobeSt, 2023).
3. Higher Cap Rates and Lower Property Values
As interest rates rise, cap rates (the return investors expect) increase, lowering property values. Developers see reduced profits when selling completed projects.
Example: A commercial building valued at $50 million with a 5% cap rate loses $10 million in value if cap rates rise to 7%.
4. Slower Leasing and Sales Activity
Higher mortgage rates make homeownership more expensive, reducing demand for new residential units. Commercial tenants also hesitate to sign long-term leases, affecting developer revenues.
Example: Mortgage rates above 7% in 2023 led to a 20% decline in new home sales nationwide (National Association of Realtors, 2023).
Strategies to Manage Higher Interest Rates
1. Lock in Fixed-Rate Financing
Developers can secure long-term, fixed-rate loans to avoid rising interest costs and stabilize project budgets.
2. Use Alternative Financing Methods
Options like private equity, joint ventures, and tax credits can reduce reliance on traditional bank loans.
Example: A multifamily developer in Florida used tax-exempt bonds to finance 40% of a project, lowering borrowing costs by 2% (Affordable Housing Finance, 2023).
3. Reduce Development Costs
Optimizing designs, using modular construction, and securing bulk material purchases can help offset rising financing costs.
4. Focus on High-Demand Markets
Developers should prioritize projects in markets with strong job growth and housing demand, ensuring stable returns.
Conclusion
The impact of Federal Interest Rates on development costs is defining the development landscape, increasing financing costs and reducing project feasibility. However, strategic planning, alternative financing, and cost-saving measures can help developers navigate these challenges. Staying informed and proactive ensures long-term success in a high-interest-rate environment.
Would you like more details on specific financing strategies or regional impacts?